Handy Suggestions To Choosing Legacy application modernization with Low-code
Handy Suggestions To Choosing Legacy application modernization with Low-code
Blog Article
Benefits Of Application Development With Low-Code In Terms Of Integration Capabilities
Low-code applications offer significant advantages in terms of integration capabilities, which are vital for developing applications that seamlessly connect with various platforms and services. Here are a few of the main benefits: Prebuilt Connectors & APIs
A Wide Variety of Connectors The Low-code software typically includes an array of connectors that are pre-built for the most popular enterprise software (e.g. CRMs, databases ERPs, cloud-based services, and more). This simplifies the process of connecting these systems.
API Integration: A lot of Low-Code platforms have out-of-box API integration tools that allow developers to quickly connect external services and data resources.
Simple to use:
Drag-and–Drop Interfaces: Many integration tasks can be easily completed using drag-and–drop interfaces. This makes it possible for developers and other non-developers to build complex systems without extensive coding.
Visual Workflow builders Visual Workflow Builders utilized to design workflows, data flow and integrations. They assist in understanding and setting up workflows more efficiently.
Standardized Integration Methods:
SOAP and restful services that support web-based services common protocols such as REST or SOAP makes integration easy with an array of software and systems.
OData Standards: OData standards permit the simple manipulation and accessibility of data across different platforms and applications.
Real-Time Data Synchronization:
Real-Time Integrations: Low code platforms are capable of handling the real-time synchronization of data among systems, applications as well as databases. This ensures that the data is always up-to date and consistent within an organisation.
Event-Driven architecture: Certain platforms can support event-driven architectures. This lets applications respond to events in real time, which is essential for dynamic and interactive apps.
Legacy System Integration:
Bridging Old Systems and new Systems Low-code platform often provides tools to integrate with existing legacy systems. This allows companies to upgrade their IT Infrastructure without overhauling the current systems.
Data Migration Tools - Built in data-migration tools make it simple to move data from old systems to applications that use low-code.
Integration of Third-Party Services:
Cloud Services Integration: Easy deployment and scaling applications is made possible by seamless integration with cloud services like AWS, Azure and Google Cloud.
Integration of Business Applications: Lowcode platforms can be used to integrate various business applications, such as Salesforce, SAP, Microsoft Dynamics etc. and create a unified workflow that spans different functions of business.
Simplified Data Processing
Unified Data Models: Certain lowcode platforms provide unification of coding models that simplify managing data as well as integration and synchronization between different systems.
Data Connectors: Data connectors that are pre-configured to permit easy access to and manipulation of data from different sources.
Security and compliance:
Low-code platforms help ensure integrations meet security protocols and standards, protecting data in transit as well as in rest.
Security Features: These platform usually have features to make sure that integrations comply with regulations, for example GDPR and HIPAA. This provides peace ofmind for businesses handling sensitive information.
Extensibility:
Custom Codes and Scripts. To meet more intricate requirements in integration, low-code platforms usually allows the use of custom scripts and code. This allows flexibility without compromising user comfort.
Plug-in Ecosystem: An ecosystem of extensions and plugins can enhance the integration capabilities that allow users to include additional functions as they need.
Overall, integration capabilities in low-code application development platforms permit them to provide a robust platform to create connected, efficient, scalable, and connected applications. They make it easier to connect different platforms. They also improve the flow of data. Follow the most popular Low-code Platform for application development blog for website examples including develop web application, low code development platforms, develop web app, app dev platform, mobile app development platforms, paas service, multiplatform mobile app development, low code platforms, rad application development, jdbc server and more.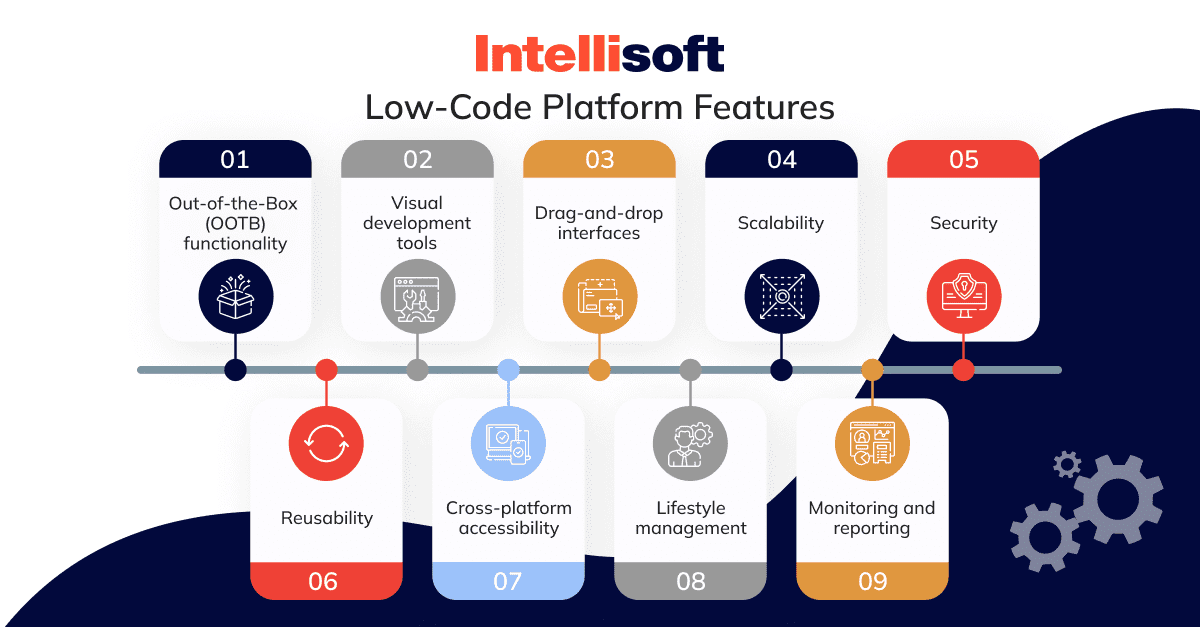
Benefits Of Low-Code Applications In Governance And Safety
Low-code applications provide a number of advantages in terms of cybersecurity and governance that are essential to ensure that applications are well-managed, managed and are compliant throughout their lifespan. Here are the most significant advantages: Centralized Governance
Unified Management Console: This low-code platform usually provides a central dashboard for administrators to control and monitor all applications, ensuring consistency governance across the organisation.
Role-Based Access Control: These platforms have robust control based on roles that allows administrators to define guidelines and enforce the rules. This guarantees that only users who are authorized have the ability to access or modify particular elements of an application.
Compliance and Regulatory Adherence
Conformity features: A lot of platforms that make use of low-code are designed to be in line to industry standards. They offer tools and frameworks to help ensure that applications are compliant with these requirements.
Audit Trails & Logging: Complete audit trails and logs can be incorporated to allow organizations to track change in access, and monitor access and compliance.
Improve Security Measures
Data Encryption. Low code platforms usually have built-in encryption for data when in transit as well as when at rest. This safeguards sensitive data.
Security Certifications A lot of low-code vendors have security certificates (e.g. ISO 27001, SOC 2 ) that demonstrate compliance with high security standards. This provides additional assurance to users.
Automated security updates
Regular Patching and Updating Lowcode platforms generally handle regular updates to security. These patches protect applications against the latest threat without requiring developer intervention.
Security Monitoring - Continuous monitoring of security is typically included. This gives real-time information and alerts about potential security threats.
Data Governance
Data Access Policies These platforms assist organizations define and implement their data access policies to ensure that only authorized users are able to access information and that it's correctly used.
Data Masking Anonymization Data Masking Tools: Built-in data masking tools and features to anonymize data help protect sensitive data, especially during development and testing environments.
Consistent Application Management:
Development and Deployment Pipelines: Low-code platforms often provide integrated deployment and development pipelines which include security checks, which ensure security remains intact throughout the application lifecycle.
Version Control - Integrated version controls help track modifications to applications and allow the application to be reversed when needed. They also help maintain the integrity and quality of the application.
User Authentication & Authorization:
Single Sign-On Support for single sign-on (SSO) and other advanced authentication mechanisms, simplifies management and increases security.
Multi-Factor Authentication A lot of platforms come with built-in support of multi-factor authentication. This adds an additional layer of security to the applications.
Policy Enforcement and Compliance Monitoring:
Low-code platforms are often pre-defined with policy templates to assist companies in implementing governance and security policies quickly.
Tools for Monitoring Compliance: These instruments provide continuous monitoring, reporting and analysis of compliance status. It is simpler to detect potential problems and take appropriate steps.
Integrate into existing security infrastructure:
Seamless Integration: Low-code platforms are designed to be integrated with existing security tools and infrastructure, like identity management systems and SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) solutions, and firewalls.
API Security: Built-in API security features safeguard the data of API users, ensure integrity of applications and provide safe integrations.
Training and Best Practices
Best practices: Many platforms provide guidelines for the development of secure applications, and offer best practices. This helps non-developers to adhere to security standards.
Some low-code providers provide security training to help users develop and maintain secure apps.
Overall, low-code application developers provide a governance and a security advantage that allows them to build and manage their applications in a safe, secure and secure manner. These platforms come with the frameworks, tools and regulatory compliance that are required to safeguard sensitive customer information, enforce policy, and maintain regulatory conformity, while also simplifying the management of and oversight over the process of developing applications. View the top rated on the main page about Legacy application modernization with Low-code for website tips including low code development platforms, application modernization software, application modernisation, app modernization, azure sql server, push alerts, cloud software applications, build with docker, rapid applications, azure sql server and more.
The Benefits Of Low-Code Programming For Developing Applications In Terms Of Restrictions And Customization
The low-code method is an unbiased method that allows for substantial customization and overcomes weaknesses. These are the main benefits: Handling the limitations
Removing Complexity Barriers
Simplified development: Low code platforms make it easier to develop by offering templates and pre-built components. This facilitates faster application deployment, even for complicated ones.
Guided Workflows Many platforms offer wizards and workflows that guide developers through the complex process. This reduces the chance of errors and ensures uniformity.
Scalability Solutions
Scalability is built into: Low-code platforms often include capabilities that permit an architecture that is scalable. Applications are able to handle higher workloads with minimal changes.
Performance Monitoring: Integrated instruments for monitoring performance and optimization help to ensure that applications are effective when they grow.
Security and compliance
Low-code platforms come with security functions like security access control that is based on roles as well as encryption and automated checks for compliance. These security features address most common security concerns.
Regular Updates: Platforms often update their security protocol and compliance policies. This helps ensure that applications are safe from threats that are constantly evolving.
Customization Capabilities:
Extensibility:
Custom Code Integration : A low-code platforms often allow the integration of custom code (e.g. JavaScript, Python) which enables developers to extend the functionalities beyond what the standard offers.
Developers can add custom modules or plugins to meet specific business needs.
APIs and Integration:
API Support - The extensive API support allows seamless integration with external services and systems and allows for complete modification.
Third-Party Services: Low code platforms have connectors built for popular third party services. This makes it easier to build and integrate applications.
Flexible Design for UI/UX
Flexible User Interfaces for Developers: Designers have the ability to alter and create user interfaces that meet specific design and usability specifications giving users a personalized experience.
Responsive Design: The built-in capabilities of responsive design make sure that apps can be adapted to different devices and screen sizes.
Making Business Logic more flexible is simple:
Visual Workflow Builders - Visual tools that allow you to build and modify workflows. business logic and processes allow developers to create complicated and customized processes without the need for programming.
Platforms can be equipped with conditional Logic which permits the development of custom scripts to address certain scenarios or business rules.
Data Management
Custom Data Modelling: Those who develop the models define custom models to fit specific application needs. They can tailor processing of data according to a company's needs.
Advanced Data Processing: Integration of advanced data processing tools and capabilities permits customization of the way data is processed and used within the application.
Balanced Limitations and Customization
Frameworks and Standards:
Low-code platforms support industry standards and best practices, which result in top-quality software that is flexible and secure.
Governance Frameworks Integrated governance frameworks help to make sure that customizations don't interfere with the integrity, compliance, or the security of an application.
Iterative Development and Feedback:
Rapid Prototyping: The ability to quickly prototype and test customizations ensures that developers can modify their designs based on feedback from users, refining the application to better meet user needs.
Continuous Improvement: Low-code platforms allow for constant improvement. They can be customized and enhanced to meet the changing needs of business.
User Empowerment
Low-code platforms empower citizen developers by allowing non-developers through intuitive interfaces to customize applications, they expand the pool of developers who can enhance and tailor apps.
Training and Support Many platforms offer an extensive amount of training and support to assist users in making successful modifications that do not compromise the application's stability or performance.
Overall, the Low-code app creation provides a framework that is strong and flexible enough to accommodate restrictions while allowing ample customisation. This allows businesses can build and maintain applications that are both functional and specifically tailored to their requirements, while keeping high standards of security, quality, and the ability to scale.